As we are in mid Feb of the year and its tax time, I thought to talk a bit on LTA and Medical reimbursement benefits. Though many of you might already know about it, let me go over it in brief for readers who have less knowledge about it.

What is LTA ?
As the name suggests, LTA i.e Leave Travel Allowance is an allowance that an employee receives form his employer for his traveling expenses while he/she is on leave. This allowance is given only for the domestic traveling, international traveling is not covered in this allowance.
There are normally two situations when employee gets this allowance :
#1. Employee receives this allowance while traveling alone or with family or dependents from his current employer.
#2. Employee receives this allowance while traveling alone or with family or dependents from his former employer after retirement or termination of job.
It is the benefit given to a salaried employee and you can claim travel expenses from any one journey in a year. Lets see some important features of this allowance:
Features of LTA
- There is a block of 4 yrs decided by govt ( current block is 2006-2009). In a block you can claim LTA for any two years. For other 2 yrs you cant claim it, so total 50,000 will be taxable in those 2 yrs.
- These blocks are not financial years (April 1 to March 31); they are calendar years (January 1 to December 31).
- If your LTA is not utilized, it gets added to your salary and you will be taxed on it.
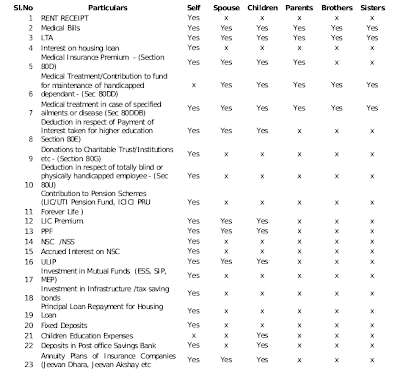
- LTA covers travel for yourself and your family. Family, in this case, includes yourself, parents, siblings dependent on you, spouse (even if your spouse is working) and children.
- The entire cost of the holiday is not covered. Only the travel costs are covered. So, whether you fly, hop on to a train or take public transport, you will have to show the ticket to claim your LTA. This means you will need to keep your air, rail or public transport ticket.
- If an employee doesn’t claim once or twice in a block year, he/she can carry forward one claim to the next block year. But the condition is he/she has to claim for that allowance in the first year only of that particular block year.
- If husband and wife both are receiving LTA then they can claim for the allowance in the same year but for different destinations.
Restrictions on claiming LTA
- You can claim on only twice in a block year
- Only actual cost of traveling is covered in this allowance
- You cannot claim LTA 2 times in a year.
- If the children are born after 1 October 1998 then you can claim for only 2 children’s traveling expenses. There are no restrictions for the children born before 1 October 1998.
Watch this video of rules and exemptions of LTA:
How much amount can claim under this allowance to get tax benefit?
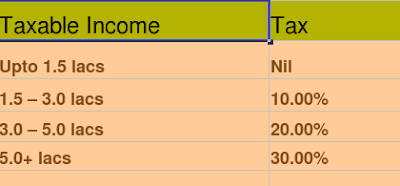
You have a limit up to which you can claim your spent amount on LTA and medical bills and save tax on that part. If you didn’t claim it, for that much amount you will be taxed .
Limit for LTA : 50,000 per year
Limit for Medical Bills : Rs 15,000 per year
So from your total salary, you can save tax on this 65000 if you want, if you don’t claim it, you will have to pay tax on this part .
Medical Reimbursement
You can also claim deductions on the medical bills for medicines and doctor visits. You just have to get the bills and submit a proofs .
The bills can be in the name of you or your dependents .
Final Note : Utilizing this benefit just requires you to keep the documents ready. many people do not claim this benefit because they are too lazy of keep the documents safe. Don’t be lazy …